Diclofenac Sodium — A Complete Medical and Pharmacological Overview
Diclofenac Sodium is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) belonging to the phenylacetic acid derivative class. It is widely prescribed for pain, inflammation, and fever management associated with musculoskeletal and autoimmune conditions.
It exhibits analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory properties by inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis, a key mediator of pain and inflammation.
ڈائکلوفیناک سوڈیم ایک غیر اسٹرائیڈل اینٹی انفلیمیٹری دوا (NSAID) ہے جو فینیلی ایسیٹک ایسڈ گروپ سے تعلق رکھتی ہے۔ یہ درد، سوزش اور بخار کے علاج میں استعمال ہوتی ہے، خاص طور پر جوڑوں اور پٹھوں کی درد میں۔ یہ پروسٹاگلینڈنز کی پیداوار کو روک کر درد اور سوجن کم کرتی ہے۔
Chemical and Structural Classification
-
Chemical class: Phenylacetic acid derivative
-
Molecular formula: C₁₄H₁₀Cl₂NNaO₂
-
Molecular weight: 318.13 g/mol
-
IUPAC name: Sodium [2-(2,6-dichloroanilino)phenyl]acetate
-
Solubility: Freely soluble in water and ethanol
-
pKa value: 4.0 (weak acid)
ڈائکلوفیناک سوڈیم کی کیمیائی ساخت فینیلی ایسیٹک ایسڈ ڈیریویٹیو پر مبنی ہے۔ یہ پانی اور الکحل میں گھل جاتی ہے، اور اس کی تیزابیت کی سطح (pKa) تقریباً 4.0 ہے، جو اس کی جذب پذیری اور اثر کی رفتار کو متاثر کرتی ہے۔
Historical Background : Developed in 1973 by Ciba-Geigy Laboratories, Diclofenac represented a new generation of NSAIDs with superior analgesic potency and fewer gastrointestinal side effects compared to traditional drugs like aspirin or indomethacin.
Since its approval, Diclofenac has been marketed in various formulations: tablets, capsules, gels, injections, eye drops, and suppositories.
یہ دوا 1973 میں سیبا-گائیگی لیبارٹریز نے تیار کی۔ پرانی NSAIDs کے مقابلے میں یہ زیادہ مؤثر اور محفوظ ثابت ہوئی۔ وقت کے ساتھ، یہ گولی، انجکشن، جل، اور آنکھوں کے قطرے جیسی مختلف شکلوں میں دستیاب ہوئی۔
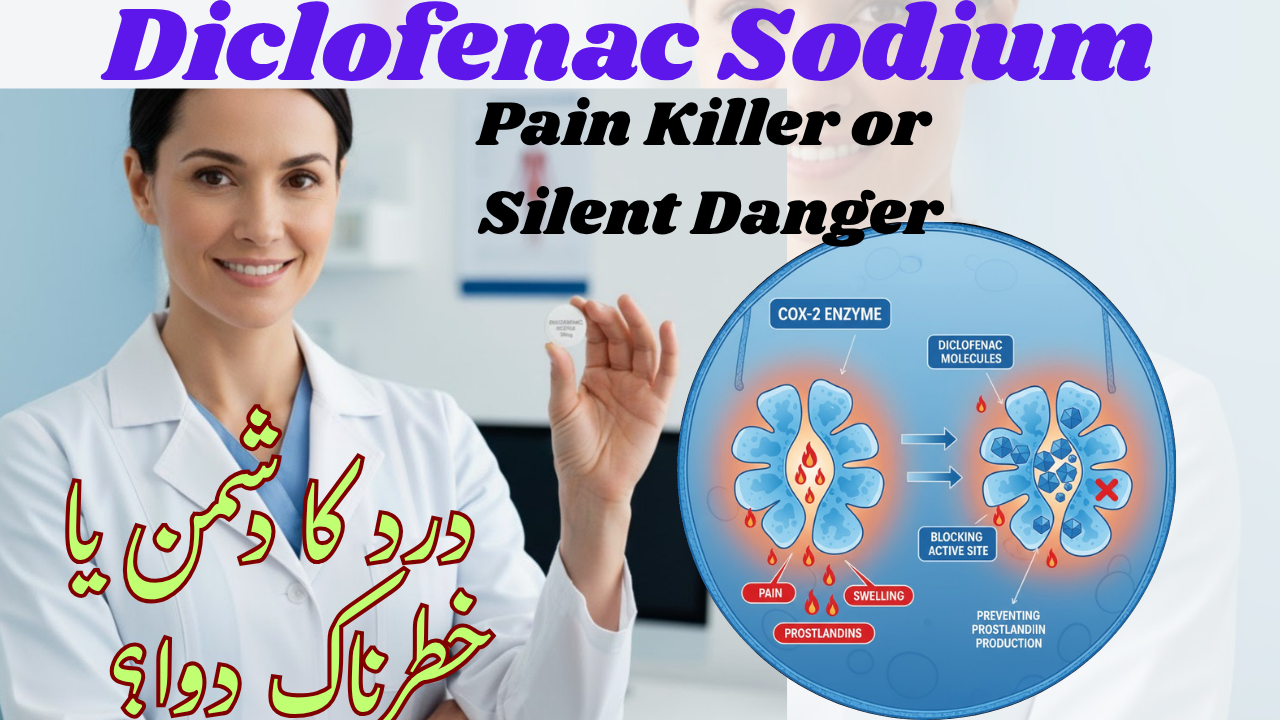
Mechanism of Action : Diclofenac primarily acts by non-selectively inhibiting both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes, thereby suppressing the conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandins and thromboxanes.
-
COX-1 inhibition: Reduces protective prostaglandins in the stomach and kidneys (increasing risk of GI side effects).
-
COX-2 inhibition: Blocks prostaglandins involved in pain, fever, and inflammation.
-
Central action: Evidence suggests Diclofenac may also act on the central nervous system by reducing substance P and modulating pain perception.
ڈائکلوفیناک سوڈیم COX-1 اور COX-2 انزائمز کو روکتی ہے، جو جسم میں آرکیڈونک ایسڈ سے پروسٹاگلینڈنز بناتے ہیں۔ ان انزائمز کے رکنے سے درد، بخار اور سوزش کم ہوتی ہے۔ کچھ تحقیقات سے پتہ چلا ہے کہ یہ دوا دماغ میں درد محسوس کرنے والے سگنلز کو بھی کم کر سکتی ہے۔
Pharmacokinetics
| Parameter | Detail |
|---|---|
| Absorption | Rapid and nearly complete after oral administration |
| Peak plasma concentration (Cmax) | Reached within 1–2 hours |
| Bioavailability | ~55–60% (due to first-pass metabolism) |
| Protein binding | >99% (mainly albumin) |
| Metabolism | Hepatic via CYP2C9 to 4′-hydroxy-diclofenac and other inactive metabolites |
| Excretion | 60% in urine, 40% in bile/feces |
| Elimination half-life | 1.5–2 hours in plasma, 6–12 hours in tissues |
ڈائکلوفیناک معدے سے تیزی سے جذب ہو جاتی ہے۔ یہ جگر میں CYP2C9 انزائم کے ذریعے میٹابولزم سے گزرتی ہے۔ اس کی زیادہ تر مقدار پیشاب یا صفرا کے ذریعے خارج ہوتی ہے۔
Pharmacodynamics
Diclofenac reduces pain by inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis both peripherally and centrally. It has dose-dependent anti-inflammatory activity and does not significantly affect body temperature in normal individuals.
It also reduces neutrophil migration, reactive oxygen species production, and inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β), contributing to its strong anti-inflammatory profile.
ڈائکلوفیناک کا اثر صرف پروسٹاگلینڈنز پر نہیں بلکہ امیون سیلز کی سرگرمیوں پر بھی ہوتا ہے۔ یہ ٹیومر نیکروسس فیکٹر (TNF-α) اور انٹرلیوکین (IL-1β) جیسے سوزش پیدا کرنے والے مادوں کو کم کرتی ہے۔
Therapeutic Indications
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis
-
Osteoarthritis
-
Ankylosing Spondylitis
-
Acute gouty arthritis
-
Dysmenorrhea
-
Migraine
-
Post-operative and post-traumatic pain
-
Soft tissue injuries and sports injuries
یہ دوا درج ذیل بیماریوں میں مؤثر ہے
رومائیٹائڈ آرتھرائٹس، اوسٹیو آرتھرائٹس، اینکیلوزنگ اسپونڈیلائٹس، گٹھیا، حیض کا درد، مائیگرین، آپریشن کے بعد کا درد، اور پٹھوں کی چوٹ۔
Dosage and Administration
-
Adults: 50–150 mg daily in divided doses.
-
Parenteral: 75 mg IM once daily (max 150 mg/day).
-
Rectal: 50–100 mg suppository daily.
-
Topical: 1% gel applied 3–4 times daily.
It should always be taken after meals to reduce gastric irritation.
بالغ افراد کے لیے روزانہ 50 سے 150 ملی گرام دوا دی جاتی ہے۔ یہ کھانے کے بعد لینا بہتر ہے تاکہ معدے پر اثر کم ہو۔
Area Under the Curve (AUC) : The AUC quantifies the total systemic exposure to Diclofenac over time. The typical AUC value is around 5.0–5.5 μg·h/mL, indicating efficient absorption. Extended-release formulations increase AUC, allowing longer pain control with fewer doses.
AUC دوا کے جسم میں موجود رہنے کے وقت اور مقدار کو ظاہر کرتا ہے۔ ڈائکلوفیناک کا AUC درمیانے درجے کا ہے، لیکن اس کی ایکسٹینڈڈ ریلیز فارم زیادہ دیر تک اثر برقرار رکھتی ہے۔
Bioavailability : Oral Diclofenac undergoes extensive first-pass hepatic metabolism, resulting in ~60% bioavailability. Rectal and parenteral routes bypass part of this effect, improving systemic availability.
زبان سے لینے پر جگر میں پہلی گزر (First-pass effect) کے باعث دوا کا کچھ حصہ ضائع ہو جاتا ہے، لیکن انجکشن یا سپوزٹری کے ذریعے دینے سے اس کی دستیابی زیادہ ہو جاتی ہے۔
Half-Life
-
Plasma half-life: 1.5–2 hours
-
Tissue half-life: Up to 12 hours
-
Steady-state concentration: Achieved within 3 days of regular dosing
Its high protein binding (99%) explains its longer duration of analgesic effect.
ڈائکلوفیناک کا پلازما ہاف لائف کم مگر ٹشو ہاف لائف زیادہ ہے، جس سے اس کا اثر کئی گھنٹے برقرار رہتا ہے۔
Overdose and Toxicity
Symptoms: Nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, metabolic acidosis, renal failure, convulsions, hepatic necrosis.
Management: Gastric lavage, activated charcoal (within 1 hour), IV fluids, correction of acid-base imbalance, and monitoring of hepatic and renal function.
زیادہ مقدار لینے سے الٹی، چکر، گردوں کی خرابی، یا جگر کو نقصان ہو سکتا ہے۔ علاج میں معدے کی صفائی، فعال کوئلہ، اور آئی وی فلوئڈز دیے جاتے ہیں۔
MIC and Antimicrobial Activity : Recent research shows Diclofenac has weak antimicrobial and antiviral effects at high MIC values (≥100 µg/mL). It interferes with bacterial DNA replication enzymes (DNA gyrase and topoisomerase). These findings are being explored for drug repurposing in resistant infections.
نئی تحقیق کے مطابق ڈائکلوفیناک زیادہ مقدار میں جراثیم کش خصوصیات رکھتی ہے، اور یہ بیکٹیریا کے ڈی این اے بنانے والے انزائمز کو متاثر کر سکتی ہے۔
Adverse and Side Effects
| System | Adverse Effects |
|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal | Gastritis, peptic ulcers, bleeding |
| Renal | Fluid retention, renal impairment |
| Hepatic | Elevated transaminases, hepatitis |
| Cardiovascular | Hypertension, edema, rare thrombosis |
| CNS | Dizziness, headache, drowsiness |
| Dermatologic | Rash, photosensitivity |
عام مضر اثرات میں معدے کا السر، جگر کی خرابی، گردوں کا بوجھ بڑھ جانا، اور سر درد شامل ہیں۔
Drug Interactions : Avoid using Diclofenac with:
-
Warfarin / Aspirin: ↑ bleeding risk
-
Lithium / Methotrexate: ↑ toxicity
-
Corticosteroids: ↑ GI bleeding
-
ACE inhibitors / Diuretics: ↓ renal function
-
Alcohol: ↑ hepatotoxicity
ڈائکلوفیناک کو ان دواؤں کے ساتھ استعمال نہ کریں: وارفرین، لیتھیئم، کورٹیکوسٹیرائیڈز یا الکحل، کیونکہ یہ زہریلے اثرات بڑھا سکتی ہیں۔
Safe Combinations Can be co-administered with:
-
Paracetamol – synergistic analgesic effect
-
Omeprazole / Pantoprazole – protect gastric mucosa
-
Muscle relaxants – for severe musculoskeletal pain
یہ دوا پیراسیٹامول، اومپرازول یا مسکل ریلیکسینٹ کے ساتھ محفوظ طور پر استعمال کی جا سکتی ہے۔
Contraindications
-
Peptic ulcer disease
-
Severe hepatic or renal impairment
-
Known NSAID hypersensitivity
-
Late pregnancy (3rd trimester)
-
History of GI bleeding or cardiovascular disease
یہ دوا ان مریضوں کو نہیں دینی چاہیے جنہیں معدے کا السر، جگر یا گردوں کی خرابی، یا NSAIDs سے الرجی ہو۔
Diclofenac Sodium remains one of the most widely used and well-studied NSAIDs. For medical students, understanding its dual COX inhibition, pharmacokinetic behavior, and clinical implications is crucial for safe and effective prescribing.
ڈائکلوفیناک سوڈیم آج بھی دنیا بھر میں سب سے زیادہ استعمال ہونے والی دوا ہے۔ میڈیکل طلبہ کے لیے اس کے اثر، میٹابولزم اور سائیڈ ایفیکٹس کو سمجھنا لازمی ہے تاکہ اس کا محفوظ اور مؤثر استعمال یقینی بنایا جا سکے۔
FAQs About Diclofenac Sodium
1. How does Diclofenac Sodium work to relieve pain?
It blocks COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes, reducing prostaglandins, which decreases pain, fever, and inflammation.
2. What are the side effects of Diclofenac Sodium tablets?
Common side effects: nausea, stomach pain, headache, dizziness.
Serious ones: ulcers, liver or kidney problems.
3. What is the half-life of Diclofenac Sodium in the body?
Its half-life is about 1.5–2 hours in plasma and up to 12 hours in tissues.
4. Can Diclofenac Sodium be used with Paracetamol?
Yes. Both can be used together for stronger pain relief when prescribed.
5. What happens if you take too much Diclofenac Sodium?
Overdose may cause vomiting, drowsiness, liver or kidney damage — seek immediate medical help.
6. How does Diclofenac Sodium affect COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes?
It inhibits both enzymes — COX-1 (stomach protection) and COX-2 (pain and inflammation).
7. What is the bioavailability of Diclofenac Sodium after oral use?
About 55–60% due to first-pass metabolism in the liver.
8. Is Diclofenac Sodium safe for long-term use?
Not usually. Long use can harm the stomach, liver, kidneys, or heart — only take under supervision.
9. What is the mechanism of Diclofenac Sodium pain relief?
It blocks prostaglandin production and reduces pain signals in the nervous system.
10. What are the signs of Diclofenac Sodium allergy?
Rash, itching, swelling, trouble breathing — stop the drug and get emergency care.